Top 5 BRC 7 Non-Conformances

Learn about updates to BRC 8.
Alchemy recently attended the BRC Food Safety America’s Conference in Tampa, Florida. Throughout the conference, ensuring compliance with BRC, amongst other regulatory and industry standards, was a top priority.
Our partners at BRC explained to attendees that conforming to BRC 7 standards should help food companies bridge any gaps in their current plan that could prevent them from meeting the much anticipated FSMA final rules. Furthermore, BRC’s Technical Director for Food Schemes David Brackston discussed the top 5 non-conformances from BRC Issue 7 to help attendees prepare for their next audit.
1. Supplier Approval
Requirement 3.8.1.2 – Food companies should be prudent in selecting suppliers of raw materials via agents or brokers. Supplier approval is now a greater focus for BRC auditors due to the prevalence of economically motivated adulteration.
Auditors are looking for a suitably rigorous approval process for each supplier including:
- Documented risk assessment
- Documented purchases from agents/brokers
- Any exceptions made in supplier approval process
Often companies make the mistake of creating a supplier approval process that is not comprehensive enough to meet the new BRC 7 requirements. Supplier risk assessments should consider every material coming into contact with product right down to packaging.
{{cta(‘e87d32a4-96a7-479f-b8e9-a9adb70dfcb7′,’justifycenter’)}}
2. Cleaning
Requirement 4.11.1 – Cleaning seems like a no-brainer, but many companies still fail to meet BRC requirements for sanitation. Remember, it’s not only what’s on the inside that counts. External premises, and overall cleanliness should be maintained as well. Some commonly overlooked areas are:
- Hand hygiene
- Foot washing stations
- Doors and seals
- Points of entry/exit
- Ceilings
- Pest control
- Air quality
Document your cleaning procedures, and provide clear notes on what expectations are to be met using:
- Clear processes for cleaning the building, plant, and all equipment
- An equipment cleaning and maintenance log
- Comprehensive environmental monitoring
- Regular chemical testing
3. Vulnerability Assessment
BRC recommends companies look to trade associations, government resources, and private resources like consultants to identify emerging and historical threats. For example, the International Association for Food Protection publishes “Food Protection Trends.” This publication can help you stay up to speed on new testing methods or the most recent hazards in the supply chain.
Note: companies should be prepared to account for the following when conducting a vulnerability assessment:
- Specific origin
- Nature of the raw materials
- Economic factors that may motivate substitution or adulteration
- Ease of access to raw materials throughout the supply chain
- Routine testing of raw materials
- Audits of routine testing
4. Raw Materials: Supplier Risk Assessment
Requirement 3.5.1.1 – Supplier approval and risk assessment go hand in hand. Companies must document a risk assessment for each raw material or group of raw materials used. Remember that raw materials include packaging.
Take these factors into consideration when developing a protocol:
- Allergens
- Foreign body risks
- Microbiological contamination
- Chemical contamination
- Potential fraud
5. Control of Chemicals
Requirement 4.9.1.1 – Careful consideration needs to be applied to non-food related chemicals within the production facility. Many companies miss the mark when it comes to crafting a detailed plan for managing chemicals—particularly in North America where it’s the number one non-conformance.
At a minimum companies should be prepared to display:
- A list of approved chemicals
- Chemical safety data and specs
- Confirmation of sustainable use in food facilities
- Documented avoidance of strongly scented products
- Highly visible labeling of chemical containers
- Designated storage area
- List of personnel with authorized access
- Sufficient training of all staff on potential hazards
How to address unsatisfactory audit results—corrective action
If non-conformities have been identified during your audit, set up a detailed plan of corrective action. This plan must be completed within 28 days of the unsatisfactory audit. Otherwise, certification will not be issued. Simply focusing on the actual issue will not suffice. Be prepared to provide proof of your root cause analysis in the corrective action plan.
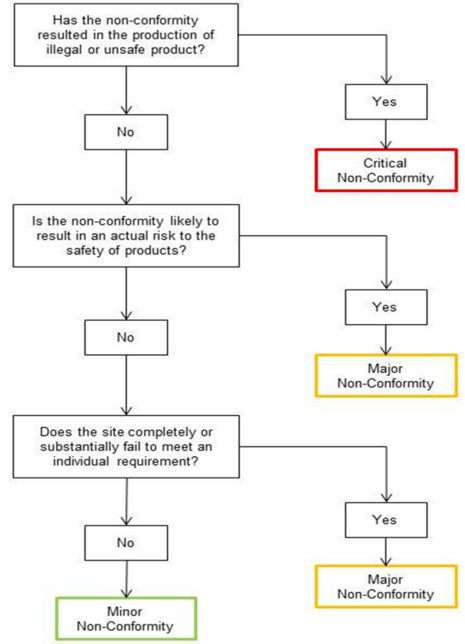
Photo Credit: British Retail Consortium
Address the issue, but find out what went wrong in the first place so you can demonstrate how you plan to avoid a repeat performance. The more documentation and more detailed your plan, the better.
Final Thoughts
As we all know, compliance is not a ‘set it and forget it’ initiative – it requires careful attention and continuous improvement. For help achieving BRC certification and keeping your plant audit-ready 24/7, we recommend contacting expert consultants.

Alchemists engage with BRC attendees in Tampa, FL
Requirement 5.4.7 – Be prepared to prove your facility has taken reasonable measures to ensure the integrity of raw materials. Affirm all raw materials carry little risk of adulteration or substitutions.






